Table of Contents
ToggleHow To Generate Consumer Engagement with Multilingual Content Optimization?
How does optimizing content generate consumer engagement? According to Outgrowco, 86 per cent of buyers are willing to pay more for a better customer experience. 64% of customers expect tailored engagements based on past interactions.
And, 54% of customers think that companies should fundamentally transform how they engage. When it comes to customer engagement, you need a strategy that transforms how your customers will engage with your brand. One way to do that is through content marketing.
At Tomedes, a translation company, that relies heavily on multilingual, it takes on a different form. Today we’ll run through them using real-life examples of content optimization, and why you need a translation company for content optimization.
What Is Localization and How Is It Different From Translation?
Localization is different from translation because one handles words while the other handles attributions. How? Well, translation is the transformation of one language to another language. Meanwhile, localization is the attribution of your content or your website, or anything really, into the culture, geographic area, or specific culture group you would like to target.
Localization is a far wider-reaching process than translation. While translation deals with the direct word choices in both the target language and the source language, localization deals with tweaking the aspects of videos, content, images, and more, so that it becomes suitable for the target audience. This is why translation companies need to hire not just language experts but those familiar with the target culture.
This means tweaking the subject matter to go along with the respective culture, news, and trending topics that are part of the target culture. So, spelling, grammar, punctuation, times, dates, and currencies should be localized. So too should the content, which should be a topic that the target audience is familiar with. That should be the aim of all translation companies.
What Is Content Optimization?
Content optimization is the process of writing content in a way that will reach the largest possible audience. It is making sure that keywords are present, that there are meta and title tags, and relevant links.
Content optimization, in a more broad sense, is optimizing the written word for use on the internet, such as websites, blogs, and social media. Content optimization is working with SEO optimization and creating the best possible outcomes for user engagement.
The Content optimization is a broad subject that covers email marketing, blog posts, social media posts, and more. It includes optimizing those types of content with SEO.
What Is Global Content Optimization And What Does SEO Have To Do With It?
For most needs, what global content optimization would entail online or website content. So, global content optimization would be optimizing for the internet and optimizing to reach the largest possible target audience. “The process of optimizing content should include making sure associated keywords are present, adding meta and title tags, and relevant links,” says Campaign Monitor.
The process of optimizing content for multilingual websites goes beyond keywords but relies on a TON of keyword research, site structure strategy, competitor analysis, location analysis, and more.
For multilingual websites, global optimization is the key to being able to adapt your content for an international audience. There are a few steps you can take to optimize your content via international SEO tactics and with the help of translation companies.
1. Site Structure – For the optimal multilingual site structure, your site should have options for different languages, where they are a dropdown menu of different countries or a menu bar of different languages. The site structure of your website should be optimized for content when you’re catering to different languages. Examples of site structures include country code top-level domain (ccTLD), subdomains, and subfolder/subdirectory.
2. Locales – Taking locales into consideration is a process called localizing. Localizing is a way for the multilingual content to match each target location. This takes into account the cultural specifications of the language, the specificities of the location, the linguistic differences, and the topics that are particularly relevant for that region.
3. International Google – Google has different international search engines, which will rank different multilingual sites based on their locations. As many as 46% of searches are local, according to Chatmeter.
4. International Keyword Research – International keyword research is just that–keyword research for targeting specific keywords for a certain country. Each of the countries that you have targeted have their own keyword research. You can filter keywords, on tools such as Google’s Keyword Planner, via country/region or language.
5. Creating Optimized Content – And lastly, you’ll create optimized content tailored to your locale and language. This means that you’ve done your research on the best content to feature for your locale and it also means that your keywords will be present. Optimized content doesn’t just mean the presence of keywords, however, but the presence of keywords that are relevant to your niche and your region or language. Your overall content must also be relevant to your location, translated into the target language.
How to Optimize Content: Tactics from a Translation Company
A translation company has the best practices when it comes to optimizing content for multilingual audiences. That’s because they normally help clients in dealing withn content for multiple languages. One of the best examples is the content optimization process used by Tomedes, a translation company, which specializes in multilingual content optimization. They start by getting a clear picture of how users search for the specific google domain where their target locale is present. Once they ascertain that there is demand, keyword research would follow. They would then create optimized content, complete with the meta title, meta description, the title tags, and the keywords, for each target locale at hand, based on the research we’ve done prior. It all comes together when they do testing for the locales, testing for its specificity relative to the locale.
In a few instances, the company had clients looking to optimize their content for Indonesia. Tomedes did a couple things for the preliminary considerations for turning on Indonesian company’s website multilingual. The first thing they did was look at their site structure:
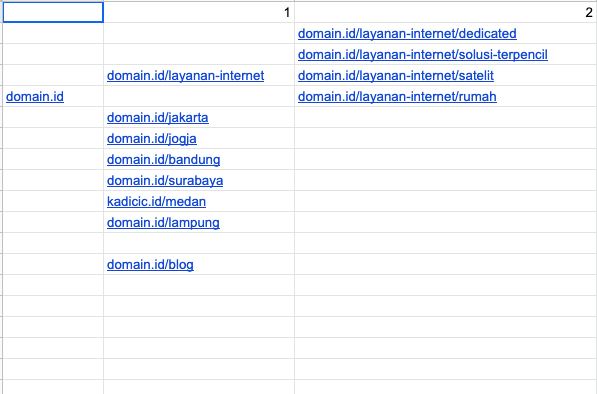
The client had a primary domain, and then they suggested 8 subdomains to go with their website, which was all based on locations, except for the blog. Then they suggested 4 more dedicated domains for their layanan domain.
Next, they performed keyword research for each location: Jakarta, Jogia, Bandung, Surabaya, Medan, and Lampung. Here’s the keyword research for Surabaya:
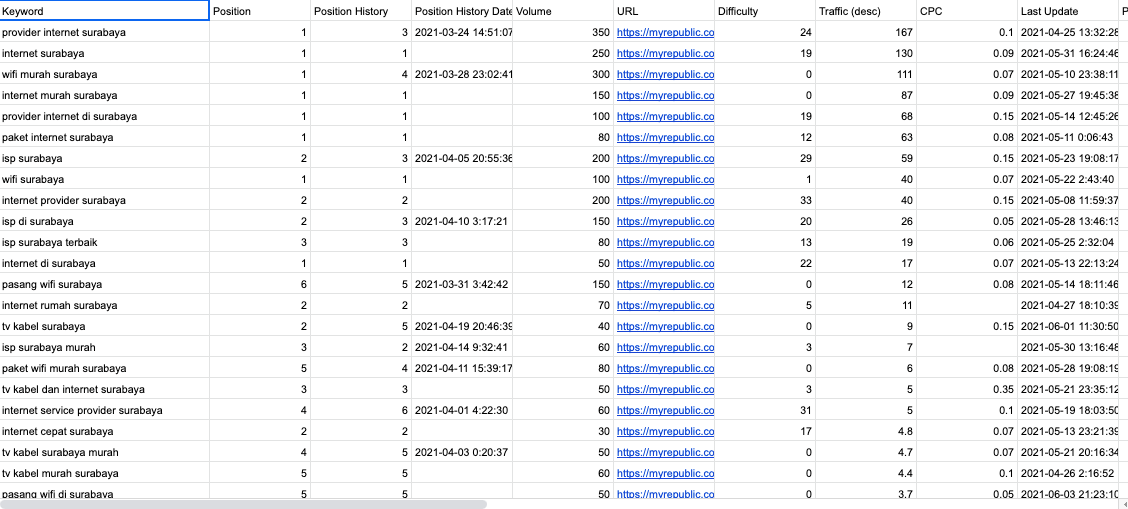
Lastly, they performed competitor analysis and saw that their client’s competitors already had websites as well. They found that, like this company, some of the competitors were also providing high-tech internet services from their website. Not all translation companies do this.
All in all, preliminary analysis saw that localized content that had to do with web solutions was best. When they saw the blogs of the competitors, they saw that their client’s content was similar as was their website structure.
Those are the preliminary considerations. The next are the steps for optimizing content that they’ve found in our over a decade of experience at Tomedes.
Step By Step Example from a Translation Company
Since optimizing content for the web has become synonymous with SEO nowadays. After years of dealing with optimizing content for the web, Tomedes has come up with three steps to content optimization. They are:
Formalizing Goals
Do you want to drive traffic for ad revenue? Do you want to get more leads? How you’re going to approach your research will depend largely on your goals. For example, in Tomedes’ experience, they were tasked with improving the content strategy of domain x.com, who was looking to expand to Indonesia. Their goal is to be one of the major internet providers in the country.
The first finalized the goals before embarking on their content optimization as part of their content marketing strategy. International SEO proved to be a major factor in determining their goals, as it gave them an outlook on the target market of Indonesia. Eventually, they saw that it was not feasible, based on their goal to generate greater leads, because they had not yet established their brand in Indonesia–so their first step, before content creation was to break into that market.
Analyzing Demand
When analyzing demand, it is always good to get an estimate of the demand by utilizing SEO tools, for example, you can get approximate traffic of 20,000 page views per month. Is Google searching the right channel to either organically promote your content or run a PPC campaign? Analyzing demand also requires looking at not just traffic but also search queries–what people are interested in, looking for, and want to know. You’ll also have to look at top of the funnel content, middle of the funnel, and bottom of the funnel.
Selecting Distribution Methods
In Tomedes’ experience, content can be optimized and distributed for SEO purposes, on blogs, news media, and other web platforms. However, social media is also a great place to distribute content, especially for those with a high following. Other distribution channels include email newsletters, press releases, ebooks/playbooks, the script for a video, and marketing intermediaries like influencers.
Content Optimization Takes Time
Content optimization involves many major factors, SEO being one of them. But any content optimization strategy is bound to take time, especially considering so many of the factors previously mentioned in this article.
Sometimes, different types of content have to be hosted in different sections of your website–and translated content will usually be on a different language page on its own.
Market research, SEO analysis, linguistic analysis, and cultural research are your friends in this endeavour, which usually takes time to analyze the content trends in your target markets.
Consumer engagement is about accommodating your consumer, each and every one of them, and this is going to take much time and effort to look at the trends for each type of consumer. Grouping them into consumer groups would be worthwhile to look at, and for international trends, grouping in terms of country or language.
It will take time, but it’s worth it.
The Last Word
Different needs suit different content. But if your need is to optimize, then you will need to determine what you’re optimizing for. Are you optimizing your content for a target audience? For a target region? For a target language, or two, or more? Are you optimizing your content for a blog, a podcast, or a specific social media channel? These questions should be answered when you’re thinking about optimizing your content. Content optimization can vary largely depending on the needs of your optimization.
However, overall, content optimization is an important part of multilingual marketing. Content optimization may sometimes be mistaken for search engine optimization, and indeed it does have similarities, but you must remember that content optimization deals with content. And as they all say, content is king. In that case, optimizing the text, headings, and meta titles and descriptions in your content is integral. One thing to remember as well is that content isn’t just text, but images and videos as well.
With the various consumer metrics, not only will you see that your content is optimized, but that it’s optimized for a certain region and language. Multilingual support is important to consumers, especially those who don’t necessarily know English.
Shashi Teja
Related posts
Hot Topics
Everything You Need to Know About a Savings Plan in 2025
A savings plan is a financial tool that offers the combined benefits of insurance & growth. This ensures financial security…
Mobile Threat Defense: The Silent Shield Behind Every Secure App
Mobile apps are found everywhere in India’s rapidly developing digital landscape—from banking and online shopping to healthcare and learning. And…



